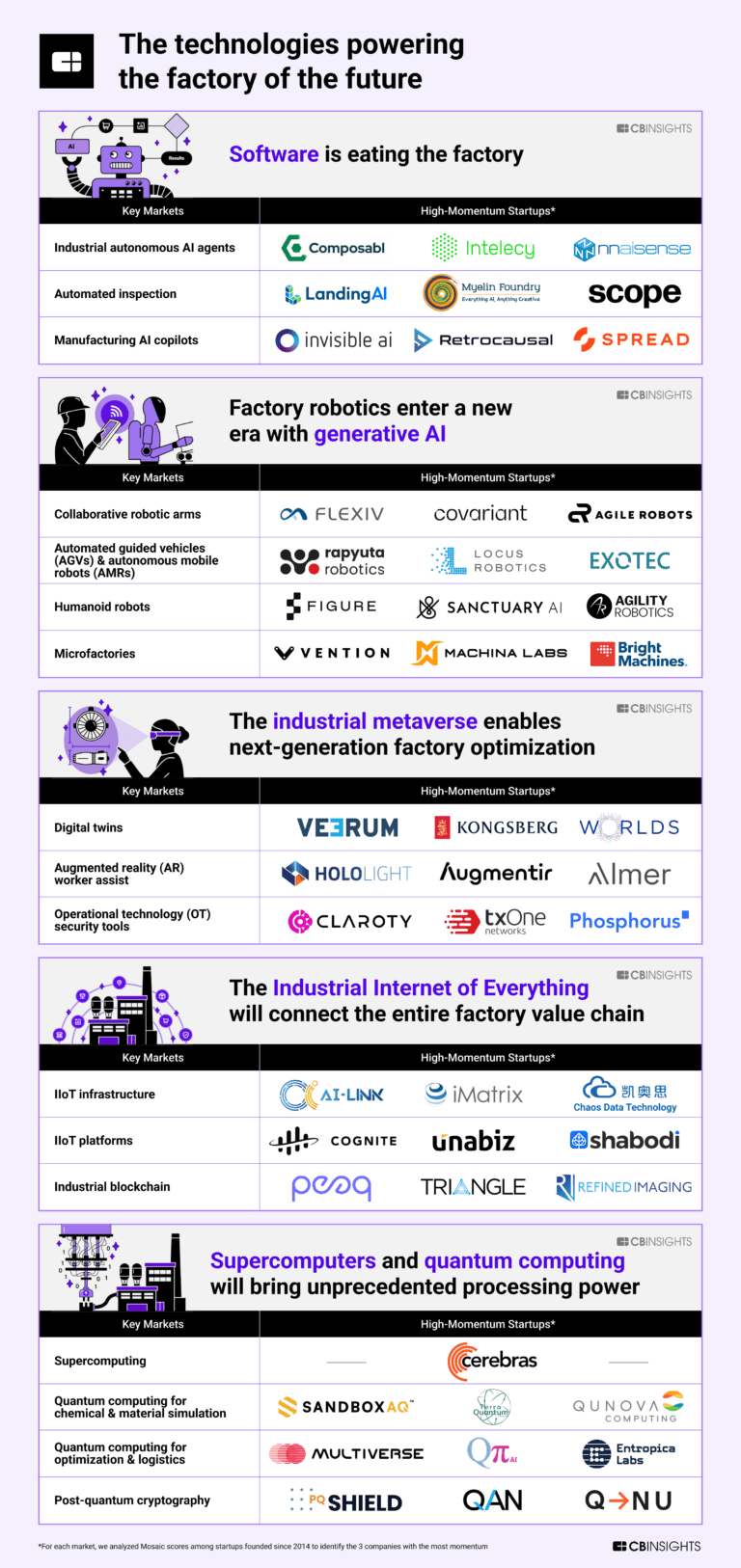
Covariant
Founded Year
2017Stage
Series C - II | AliveTotal Raised
$207MLast Raised
$80M | 2 yrs agoMosaic Score The Mosaic Score is an algorithm that measures the overall financial health and market potential of private companies.
-70 points in the past 30 days
About Covariant
Covariant develops automation solutions using artificial intelligence (AI) in the robotics sector. Its main offering, the Covariant Brain, is an AI platform intended to allow robots to pick various items autonomously from day one, supporting warehouse operations. Its technology is used by fulfillment companies to improve operational processes and tackle labor challenges. It was formerly known as Embodied Intelligence. It was founded in 2017 and is based in Emeryville, California.
Loading...
Covariant's Product Videos


ESPs containing Covariant
The ESP matrix leverages data and analyst insight to identify and rank leading companies in a given technology landscape.
The collaborative robot arms market develops, produces, and deploys robotic arms designed to work alongside humans collaboratively. They are equipped with advanced sensors and safety features that allow them to operate close to humans without physical barriers or protective cages. They are designed to assist humans in tasks such as assembly, pick-and-place operations, packaging, and material handl…
Covariant named as Challenger among 15 other companies, including ABB, DENSO, and Epson.
Covariant's Products & Differentiators
Robotic Putwall
ln batch picking operations for apparel, health & beauty, general ecommerce, etc., Covariant robotic solutions can autonomously sort items into an order bin or putwall — freeing up workers for more value-added tasks while increasing throughput.
Loading...
Research containing Covariant
Get data-driven expert analysis from the CB Insights Intelligence Unit.
CB Insights Intelligence Analysts have mentioned Covariant in 3 CB Insights research briefs, most recently on Apr 11, 2025.
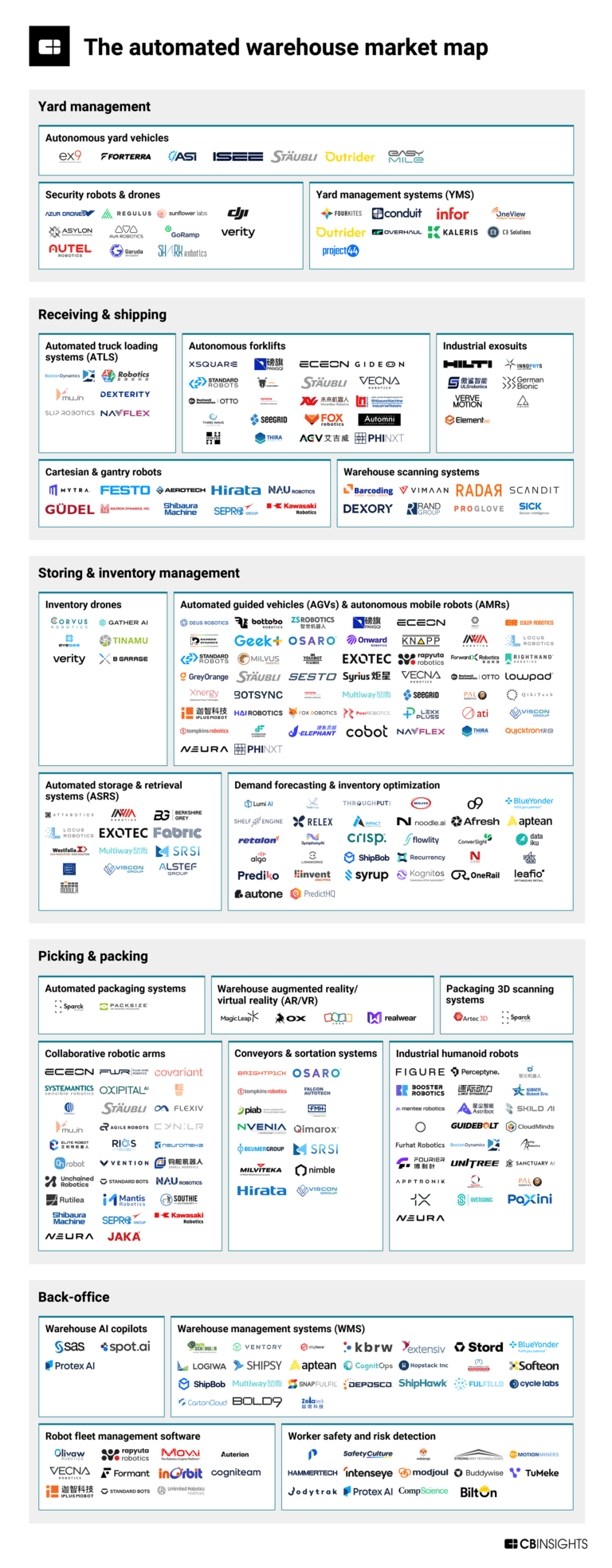
Feb 13, 2025
The automated warehouse market mapExpert Collections containing Covariant
Expert Collections are analyst-curated lists that highlight the companies you need to know in the most important technology spaces.
Covariant is included in 7 Expert Collections, including Robotics.
Robotics
2,703 items
This collection includes startups developing autonomous ground robots, unmanned aerial vehicles, robotic arms, and underwater drones, among other robotic systems. This collection also includes companies developing operating systems and vision modules for robots.
AI 100 (All Winners 2018-2025)
300 items
The winners of the 4th annual CB Insights AI 100.
Future Unicorns 2019
50 items
Supply Chain & Logistics Tech
754 items
Advanced Manufacturing
6,695 items
Companies in the advanced manufacturing tech space, including companies focusing on technologies across R&D, mass production, or sustainability
Future of the Factory (2024)
436 items
This collection contains companies in the key markets highlighted in the Future of the Factory 2024 report. Companies are not exclusive to the categories listed.
Latest Covariant News
May 28, 2025
Automation and robotics are revolutionizing next generation pack assembly by combining AI-driven vision, collaborative robots and automated guided vehicles to streamline everything from cell stacking to module joining and final pack validation. Meanwhile, Manufacturers are weighing their capital investments against long-term labor savings, zeroing in on the tasks robots are ready to own today and those that still require human judgment. Many pilot builds start semi-automated, with humans guiding robotic arms through complex, high-voltage puzzles. As vision systems gain accuracy and cobots learn through machine-learning loops, production shifts toward highly-automated, multi-variant lines that assemble cells in seconds, with no room for error. Yet winning automation strategies are not about going fully lights-out. They focus on right-sizing automation, placing robots where they generate the most value, and empowering people where adaptability and problem-solving matter most. Successful pack assembly systems balance throughput, quality, and safety in real time. Integration matters more than buying the most sophisticated robots; it comes down to seamless software logic, modular failover paths, and smart system design. For example, Covariant’s AI-powered robot arms now handle goods-to-person bin picking and kitting with rates that exceed human performance, thanks to its Robotics Foundation Model, which ingests text, images and sensor data to improve grasping and sorting over time. AI vision is transforming blind robotic executors into adaptive learners. Zivid’s 3D color cameras capture high-resolution point clouds that guide cobots through pick-and-place and de-palletizing tasks. A leading battery manufacturer deployed an AI vision defect detection system that initially struggled with limited data, but by generating synthetic defect images and retraining deep-learning models, it now identifies surface cracks and weld anomalies with over 98 percent accuracy. Redundancy and fault tolerance are baked into modern pack lines. Robotics integrators design parallel robot paths along with shadow stations that can seamlessly take over if a unit fails. Automated guided vehicles ferry modules between work cells, while software monitors real-time throughput and reroutes tasks around bottlenecks. Ford’s Livonia transmission plant , for instance, increased assembly speed by 15 percent when it layered AI-driven motion optimization onto existing robots, showing how incremental improvements can deliver big gains without ripping out entire systems. Automation and robotics also unlock new safety and compliance capabilities. Automated guided vehicles eliminate pedestrian-robot collisions by mapping human traffic patterns, and power-triggered safety zones automatically halt nearby robotic arms if workers enter restricted areas. In regulated sectors like aerospace and energy, these protocols ensure every weld and fastener meets strict standards, while digital twins run parallel simulations to validate process changes before they hit the production floor. Capital investment remains a hurdle, especially for midsize manufacturers. Deploying a full suite of cobots, vision systems and AGVs can cost millions of dollars up front. But labor savings compound over time. Amazon’s $100 billion automation push across its fulfillment network reduced order fulfillment costs by 25 percent and is expected to save the company $10 billion annually by 2030, even after factoring in maintenance and software licensing. Looking ahead, IoT sensors and data analytics will turn routine quality checks into predictive maintenance engines. Embedded sensors can monitor torque during module joining and report deviations before they cause downtime. Analytics platforms will aggregate this data to flag drift in assembly parameters, triggering on-the-fly calibration or scheduling robot servicing. Eventually, engineers will rely on real-time dashboards that blend sensor feeds, digital twin alerts and production metrics, making surprise line stoppages a thing of the past. The future of pack assembly lies in hybrid work cells where humans and robots collaborate seamlessly. Robotics take on repetitive, precision-driven tasks, freeing engineers to focus on process innovation and continuous improvement. As AI models learn from every cycle, robots will adapt to new cell formats and materials with minimal reprogramming. By right-sizing automation, investing in smart integration and embracing AI-driven vision, manufacturers can unlock safer, faster and more flexible pack assembly lines that meet today’s demands and tomorrow’s uncertainties. Kartik Gurav is a manufacturing engineering leader specializing in battery pack production systems, automation strategy, and global equipment ramp-ups. With over a decade of experience spanning high-speed consumer goods and next-generation electric vehicle platforms, Kartik has led critical production launches that saved hundreds of millions in cost and enabled gigawatt-hours of new capacity. Kartik holds a Master’s degree in Product Development Engineering from the University of Southern California and certifications in Six Sigma, Project Management, and Smart Manufacturing.
Covariant Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When was Covariant founded?
Covariant was founded in 2017.
Where is Covariant's headquarters?
Covariant's headquarters is located at 5905 Christie Avenue, Emeryville.
What is Covariant's latest funding round?
Covariant's latest funding round is Series C - II.
How much did Covariant raise?
Covariant raised a total of $207M.
Who are the investors of Covariant?
Investors of Covariant include Amplify Partners, Radical Ventures, Index Ventures, CPP Investments, Gates Frontier and 14 more.
Who are Covariant's competitors?
Competitors of Covariant include Nimble, Sileane, AICA, Dexterity, RightHand Robotics and 7 more.
What products does Covariant offer?
Covariant's products include Robotic Putwall and 3 more.
Who are Covariant's customers?
Customers of Covariant include Capacity, GXO, Obeta and McKesson.
Loading...
Compare Covariant to Competitors

Berkshire Grey develops artificial intelligence (AI) enabled enterprise robotics aimed at the fulfillment and logistics sectors. The company provides solutions that assist in tasks such as identifying, picking, sorting, packing, and moving goods within a warehouse. Berkshire Grey's technology targets warehouse operations, focusing on the needs of retailers, e-commerce, and logistics enterprises. It was founded in 2013 and is based in Bedford, Massachusetts.

inVia Robotics provides warehouse automation solutions within the logistics and supply chain industry. The company offers products including autonomous mobile robots, an artificial intelligence (AI) powered warehouse intelligence platform, and a modular goods-to-person system aimed at improving warehouse productivity and operational efficiency. inVia Robotics serves e-commerce distribution centers and supply chain operations, providing a robotics-as-a-service model that integrates with existing infrastructure. It was founded in 2015 and is based in Westlake Village, California.

RightHand Robotics provides robotic piece-picking solutions for order fulfillment in industries like e-commerce and pharmaceuticals. Its offerings include a robotic system for item picking, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, along with fleet management and customer support services. Its technology integrates into existing workflows for order fulfillment. It was founded in 2015 and is based in Charlestown, Massachusetts.

Scallog provides robotic solutions for order preparation within the logistics sector. The company offers products including mobile robots, shelving systems, and workstations that are intended to automate and optimize warehouse operations. Scallog's solutions are utilized in e-commerce, industrial, retail, fashion, consumer goods, and cosmetic-pharmaceutical sectors. It was founded in 2013 and is based in Nanterre, France.

Plus One Robotics provides robotic and automated material handling solutions within the logistics and warehousing industry. The company offers services such as depalletizing, parcel induction, and palletizing, powered by PickOne artificial intelligence (AI) software and supported by human oversight to enhance productivity. Plus One Robotics serves sectors including general merchandise, parcel & post, and third-party logistics (3PL). It was founded in 2016 and is based in San Antonio, Texas.
Bleum Robotics provides software and IT development services across industries including high-tech, financial services, and telecommunications. The company focuses on development centers and provides services such as application development, infrastructure support, maintenance, testing, and modernization of legacy systems. Bleum Robotics serves clients in North America and Europe with a focus on delivering solutions through a delivery model. It was founded in 2001 and is based in Englewood, Colorado.
Loading...